Image Manipulation by Text Instruction
Introduction
The powerful Diffusion model, which could combine texts and image as input for text-to-image tasks and even image inpainting, show breakthrough performance on image inpainting. In this work, diverging from the traditional use of the Diffusion model in inpainting, we explore a framework that enables image manipulation: specifically, the ability to modify an image based on object attributes using textual action descriptions.
Task
We address the following action-effect prediction task. Given an image depicting an initial state of the world and an action expressed in text, predict an image depicting the state of the world following the action. The prediction should have the same scene context as the input image.
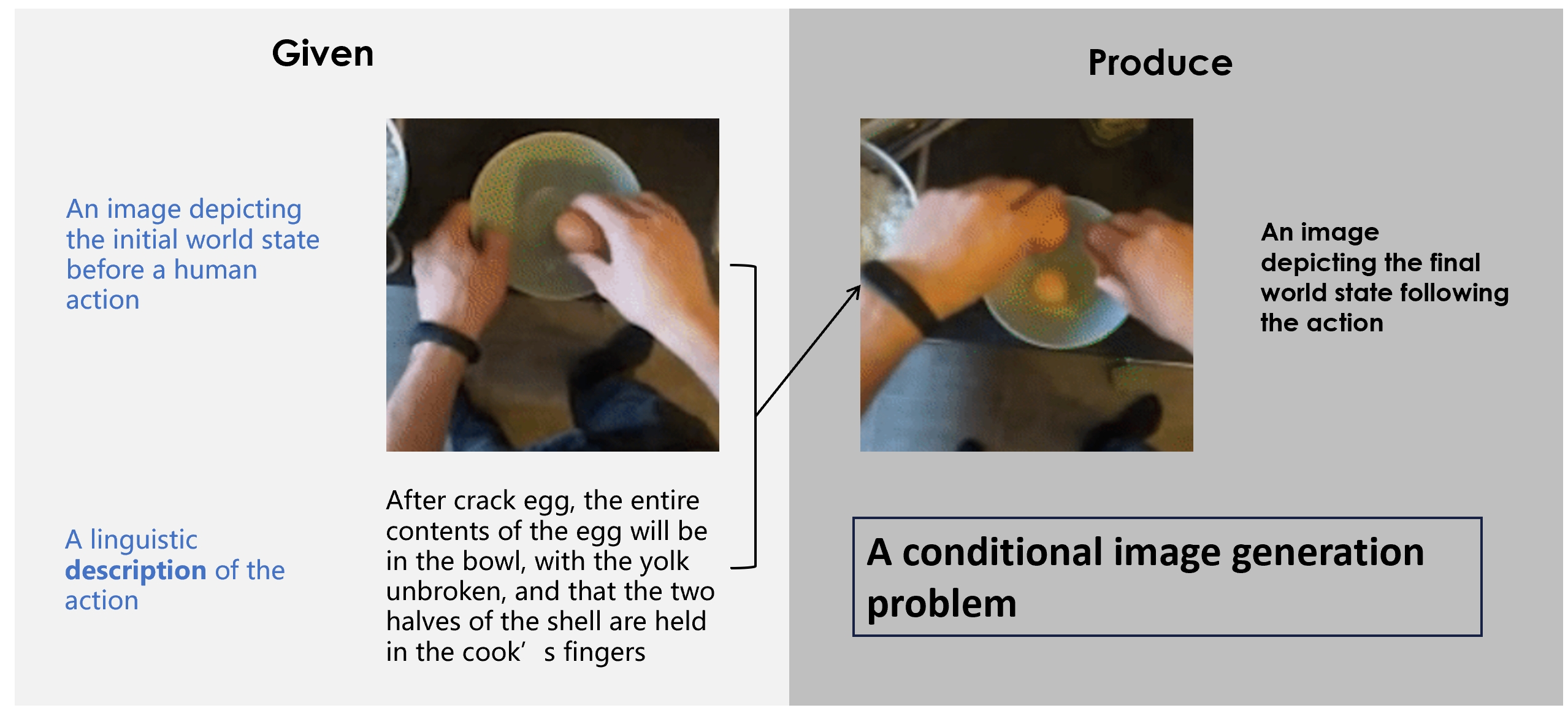
Data
There are two types of human action video datasets: those taken in the third-person and those taken in the first-person (egocentric).
- Third-person videos/images human action Datasets include UCF101, KTH, and UCFsports. These datasets cover human actions like dancing, climbing, walking, etc.
- First-person (egocentric) video datasets include Extended GTEA Gaze+ and EPIC Kitchens. The majority of the actions are first-person observers holding or manipulating objects. The actions in these two datasets are all about the preparation of meals in a realistic kitchen scenario.
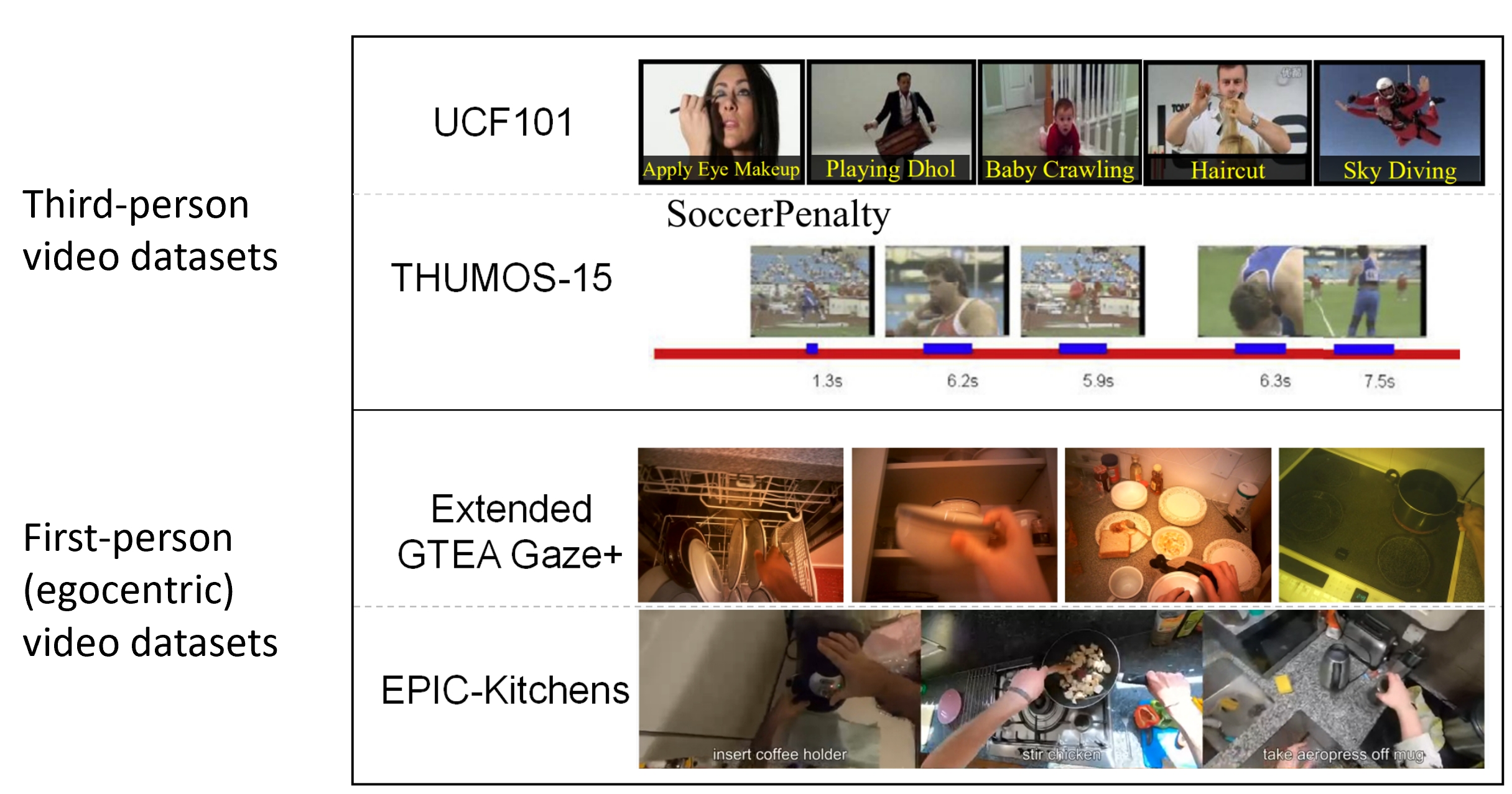
We selected egocentric videos for two reasons: most images are about manipulated objects, The publicly available version of GLIDE was trained on a filtered version of a dataset that excluded all images of humans, so may have poor performance on whole-body state change prediction.
Exploring GLIDE Model for Image Manipulation
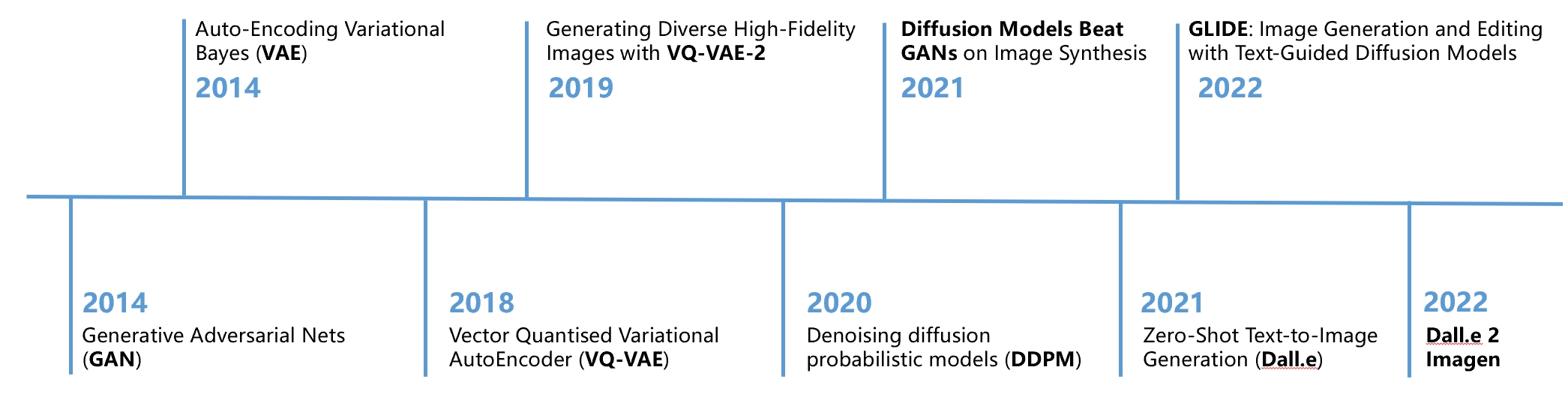
The development of image synthesis models
Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) have gained great attention since their introduction in 2014. Variational auto-encoders (VAE), which were put forward around the same time, have also increased in popularity over recent years. Following work on image synthesis using a VAE includes VQ-VAE and Dall.E. The use of diffusion models in image synthesis have recently achieved high quality results since 2020, following work GLIDE, Dalle-2, and Imagen all use diffusion based model.
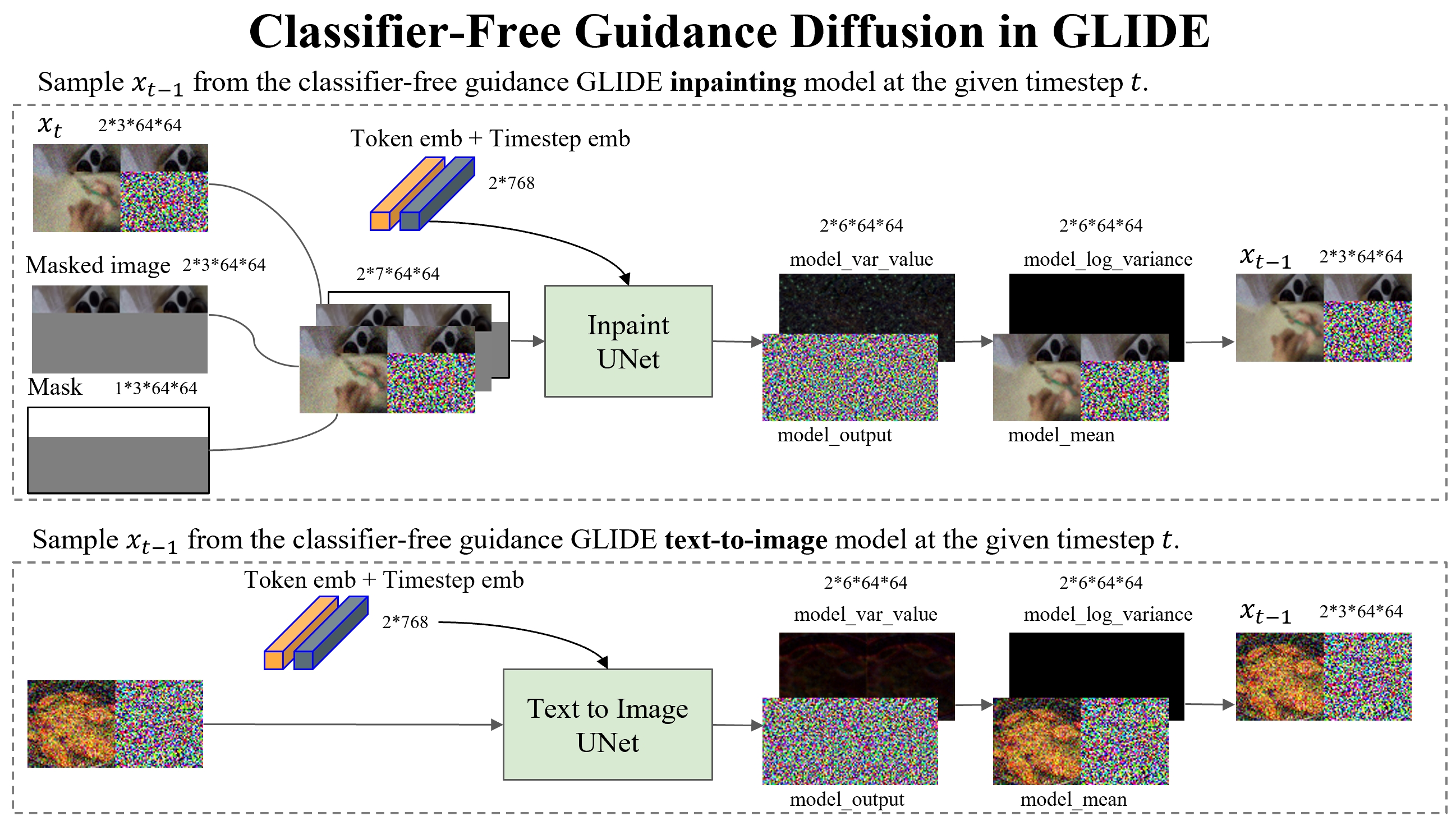
The GLIDE Model
GLIDE is a generative neural network that can synthesize (inpaint) masked areas of an image, conditioned on a short piece of text. We explore the use of the recently proposed GLIDE model for performing this task due to the following considerations.
- Can be used to perform image editing (in-painting), which means it can take both visual and textual input.
- A diffusion-based method, having shown superior performance in terms of image sample quality
- Trained on billions of images.
Methods
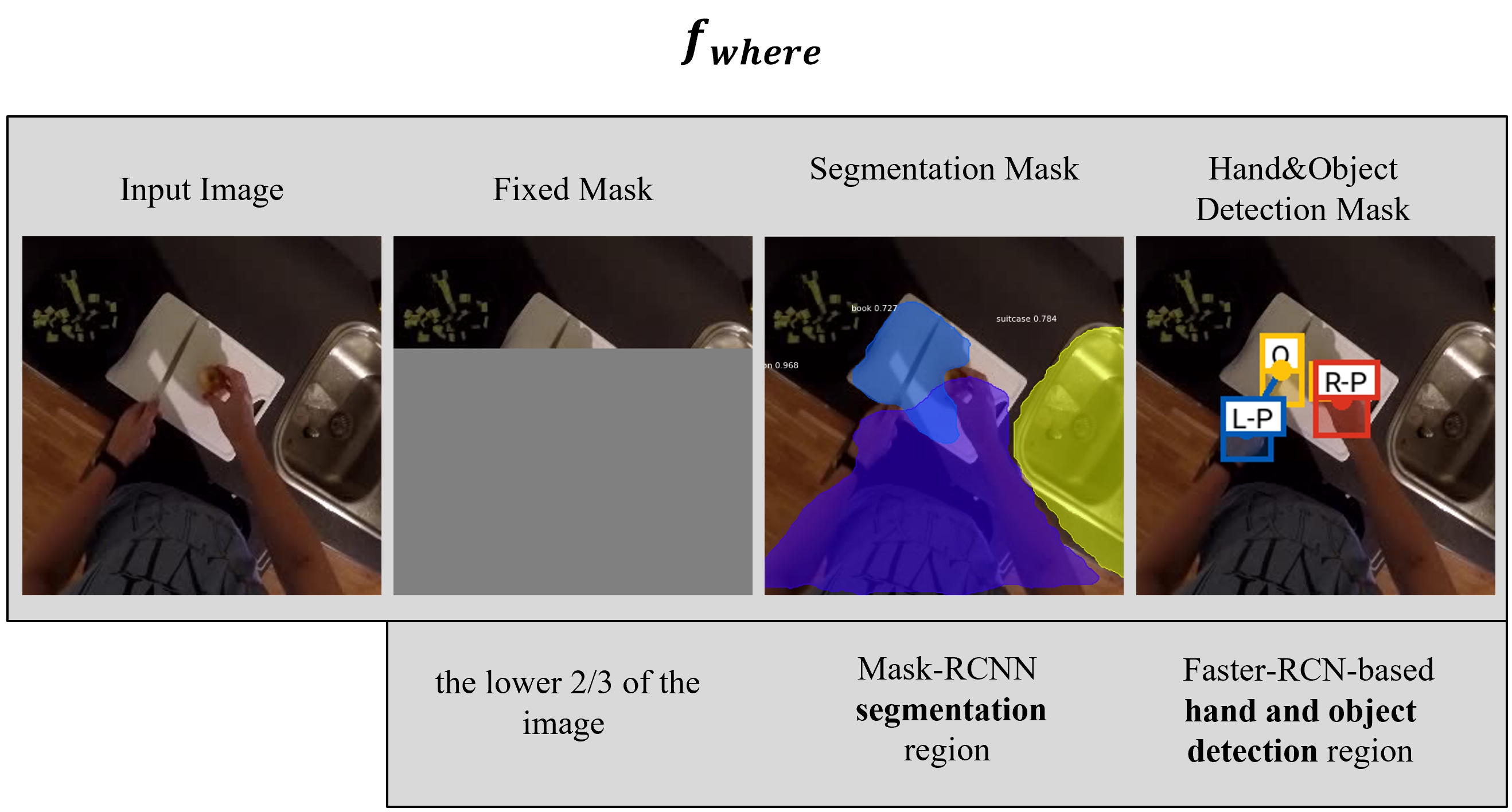
Our idea is to mask-out a region of the input image where the effect of the action is expected to occur. GLIDE is then used to inpaint the masked region conditioned on the required action. In this way, the resulting image has the same background context as the input image, updated to show the effect of the action.
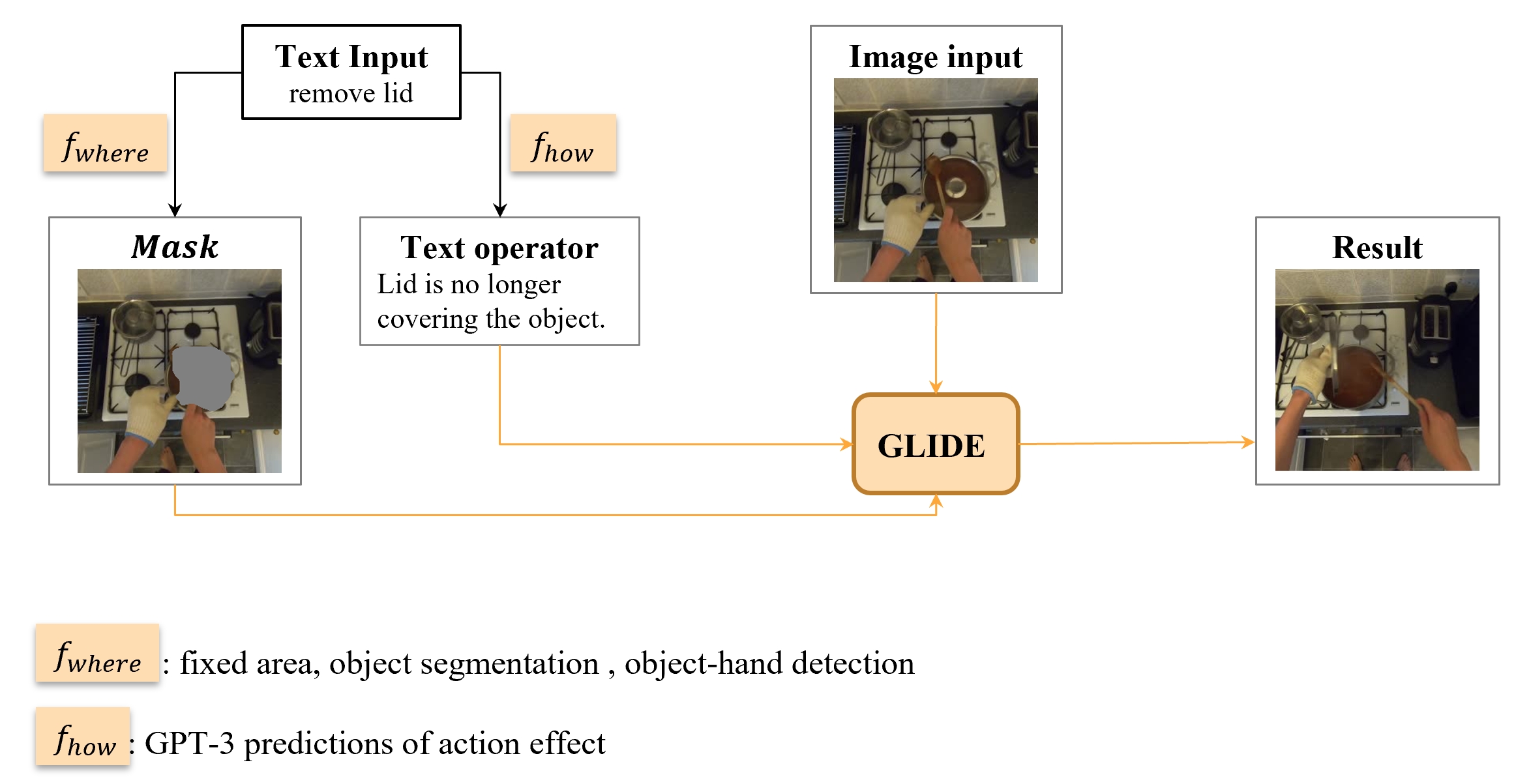

Results
We visually compare performance on the action-effect prediction task with the three mask settings and two ways of generating text prompts.
 Examples of action-effect prediction on action
Examples of action-effect prediction on action add chicken (left), cut apple (middle) and remove lid (right) with GLIDE using different masks and text prompts. Within the panel for each action are shown the original start and end frames from the dataset (top row), the three masks (2nd row), the results using the action phrase as the text prompt to GLIDE (3rd row), and the results using the effect description from GPT-3 as the text prompt to GLIDE (4th row)
We show several failure cases: some actions that involve changing the brightness of the environment rather than changing the attributes of items, e.g., turn on light; certain position-changing actions such as switch cupboard (i.e. open or close cupboard); and object-quantity-increasing actions such as cut carrots and peel garlic, the initial masked area may be insuf ficiently large to fully fill in the newly formed pieces.
 Failure examples using segmentation mask and action phrase as text prompt.
Failure examples using segmentation mask and action phrase as text prompt.
Finetuning GLIDE Model for Image Manipulation
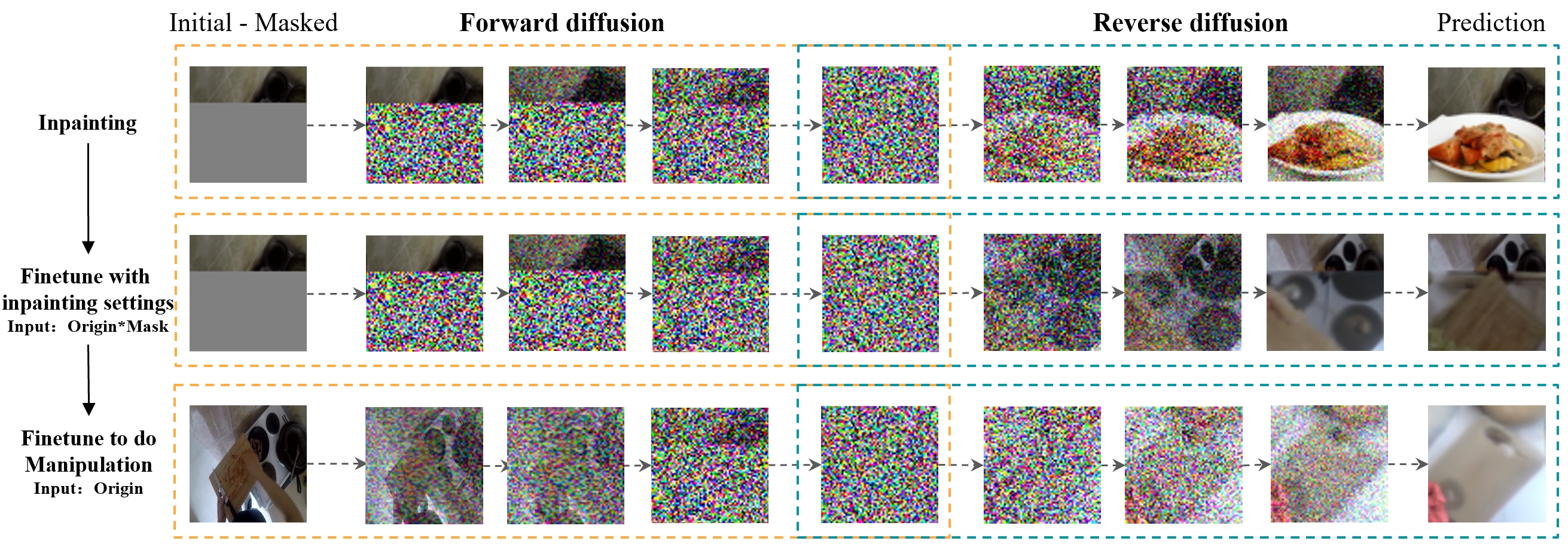
Results
We visually compare performance: 



Cross Attention in Stable Diffusion
Structure
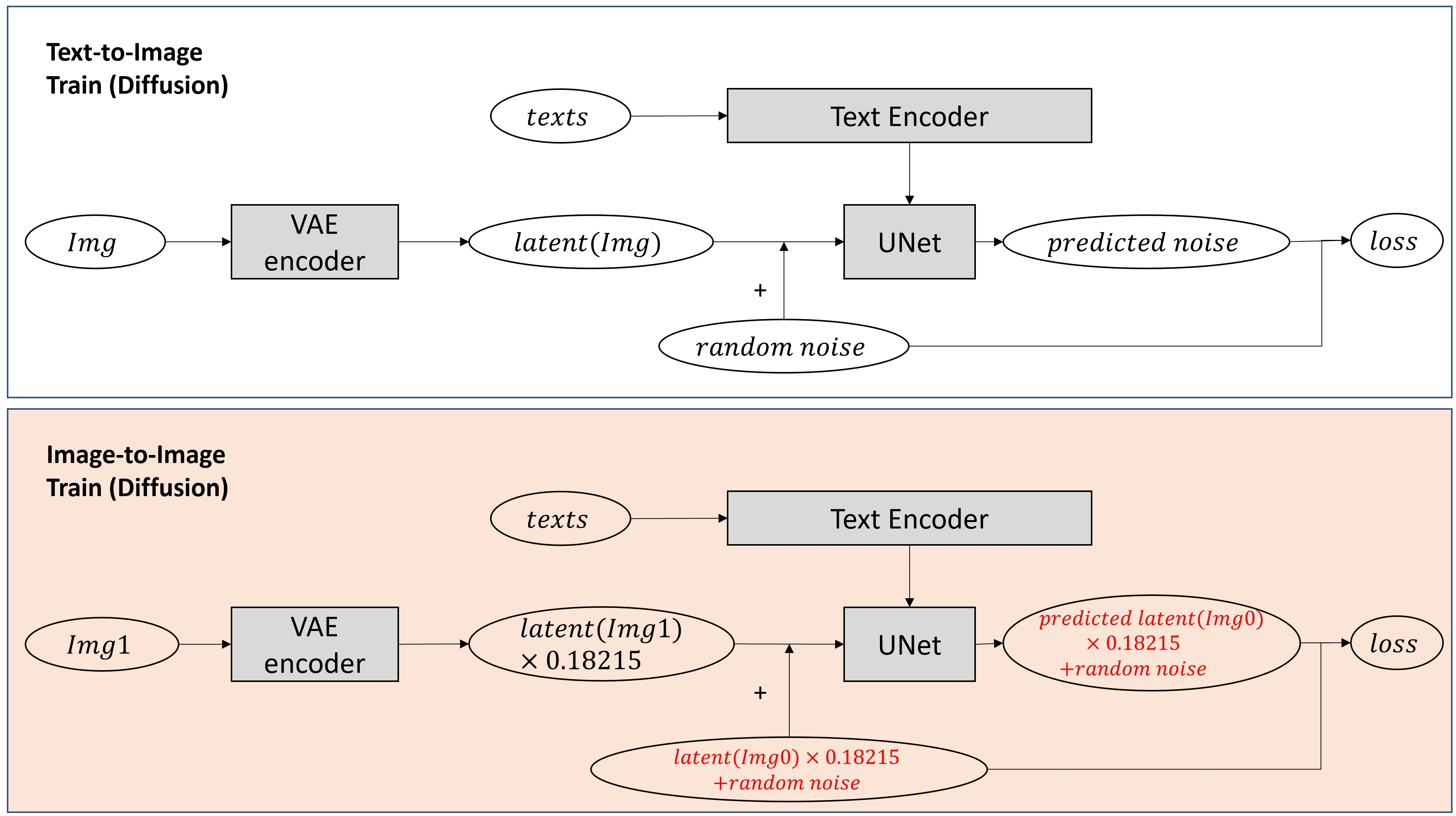
Results
Example manipulation result of Stable Diffusion with the input image and text input add chicekn. 
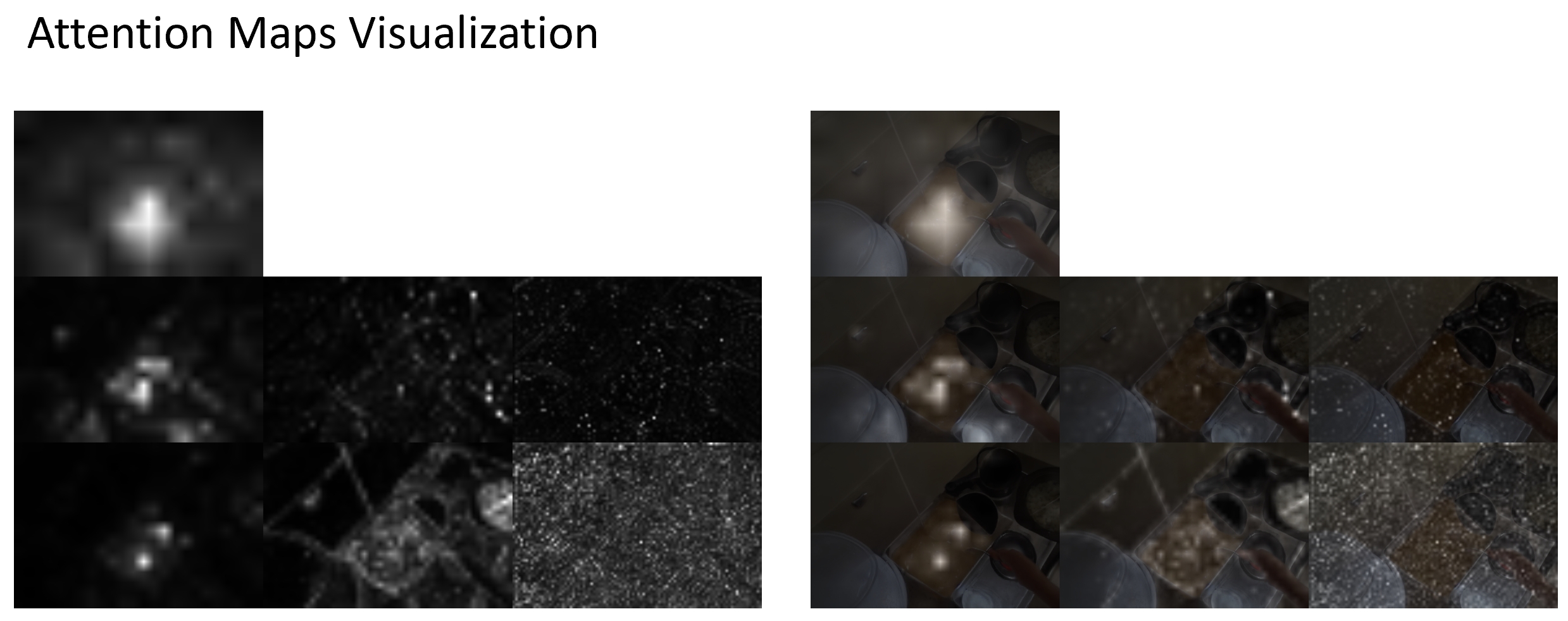
Visualizing the attention map for each token in the text input The chicken is transfered from the cutting board to the pot. 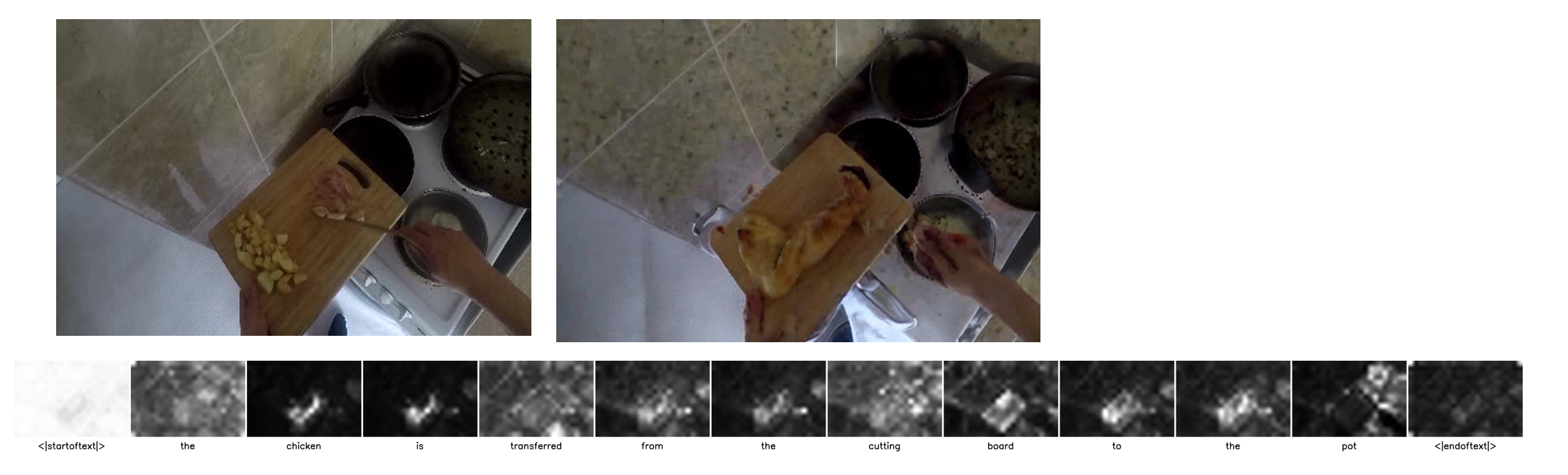
Conclusion
We explored Diffusion models’ potential on our real-world action-effect prediction task. We have shown that by optimising the mask area design and converting actions into action-effect descriptions as text prompts, the GLIDE model can create more accurate predictions that are consistent with the start world state. In future work, it would also be interesting to explore whether GLIDE could be developed to avoid the use of a mask and instead revise the whole image based on a text prompt.
